Advanced plotly
Carson Sievert
Slides: https://bit.ly/plotcon17workshop
Slides released under Creative Commons
Monthly housing sales
library(plotly)txhousing#> # A tibble: 8,602 × 9#> city year month sales volume median listings inventory date#> <chr> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>#> 1 Abilene 2000 1 72 5380000 71400 701 6.3 2000.000#> 2 Abilene 2000 2 98 6505000 58700 746 6.6 2000.083#> 3 Abilene 2000 3 130 9285000 58100 784 6.8 2000.167#> 4 Abilene 2000 4 98 9730000 68600 785 6.9 2000.250#> 5 Abilene 2000 5 141 10590000 67300 794 6.8 2000.333#> 6 Abilene 2000 6 156 13910000 66900 780 6.6 2000.417#> 7 Abilene 2000 7 152 12635000 73500 742 6.2 2000.500#> 8 Abilene 2000 8 131 10710000 75000 765 6.4 2000.583#> 9 Abilene 2000 9 104 7615000 64500 771 6.5 2000.667#> 10 Abilene 2000 10 101 7040000 59300 764 6.6 2000.750#> # ... with 8,592 more rowsAbilene monthly sales
Abilene <- subset(txhousing, city == "Abilene")p <- ggplot(Abilene, aes(month, sales, group = year)) + geom_line()ggplotly(p, dynamicTicks = "x")Abilene monthly sales, animated by year
p <- ggplot(Abilene, aes(month, sales, frame = year)) + geom_line()ggplotly(p)Works in plot_ly() as well
p <- plot_ly(Abilene, x = ~month, y = ~log(sales), frame = ~year, showlegend = F)add_lines(p)Your Turn
Part 1
Compare the output of add_lines(p, color = I("black")) with add_lines(p, color = "black"). Why is one 'right' and one 'wrong'?
Hint: Compare the output of qplot(data = Abilene, x = month, y = sales, color = I("black")) with qplot(data = Abilene, x = month, y = sales, color = "black").
Part 2
plot_ly() and the add_*() functions support a number of "special" arguments (see help(plot_ly)). They make it easier to map data to visual aesthetics in the figure reference.
Try changing the default linetype from "solid" to something else.
Hint: View(Schema$traces$scatter$attributes$line)
Animations are layer specific
p <- ggplot(Abilene, aes(month, sales)) + geom_line(aes(group = year), alpha = 0.2) + geom_line(aes(frame = year), color = "red")ggplotly(p)Easily change animation options
animation_opts( ggplotly(p), frame = 1000, easing = "elastic")Easily change button appearance
animation_button( ggplotly(p), x = 1, xanchor = "right", y = 1, yanchor = "middle")Easily change slider appearance
animation_slider( ggplotly(p), currentvalue = list(prefix = "YEAR ", font = list(color = "red")))Gapminder data
data(gapminder, package = "gapminder")gg <- ggplot(gapminder, aes(gdpPercap, lifeExp, color = continent, size = pop)) + geom_point(alpha = 0.1) + geom_point(aes(frame = year, ids = country)) + scale_x_log10()ggplotly(gg) %>% animation_opts(1000, redraw = FALSE)Your Turn
Read through this thread. Can you take what is there to make a cumulative animation of the gapminder data?
Hint: Use geom_path() over geom_point()
PS. hopefully we will have more official solution someday.
Solution is here
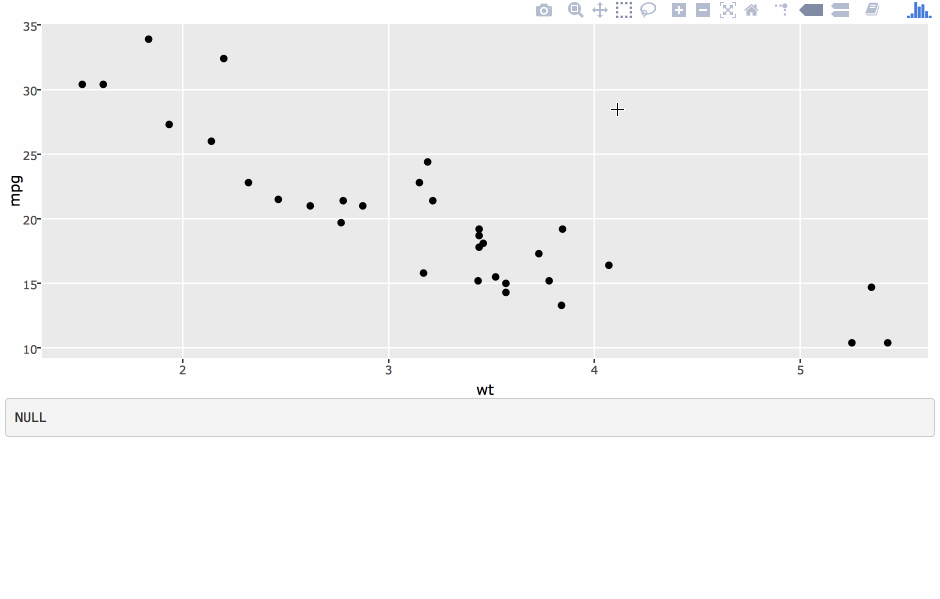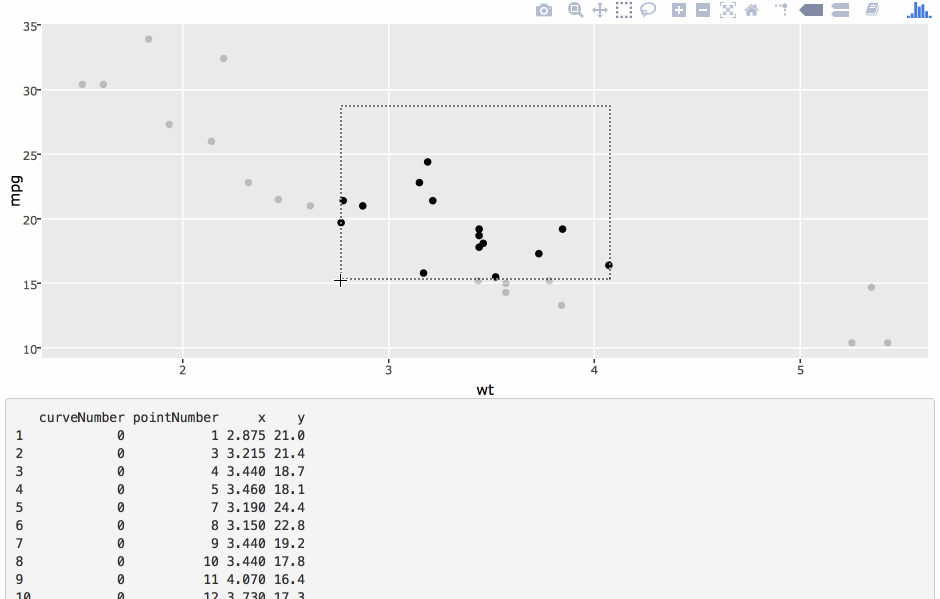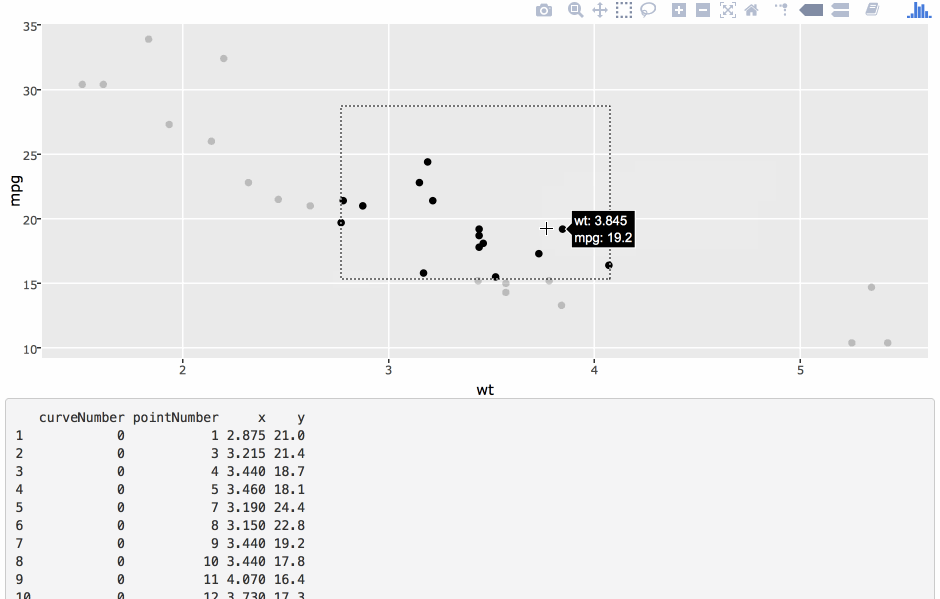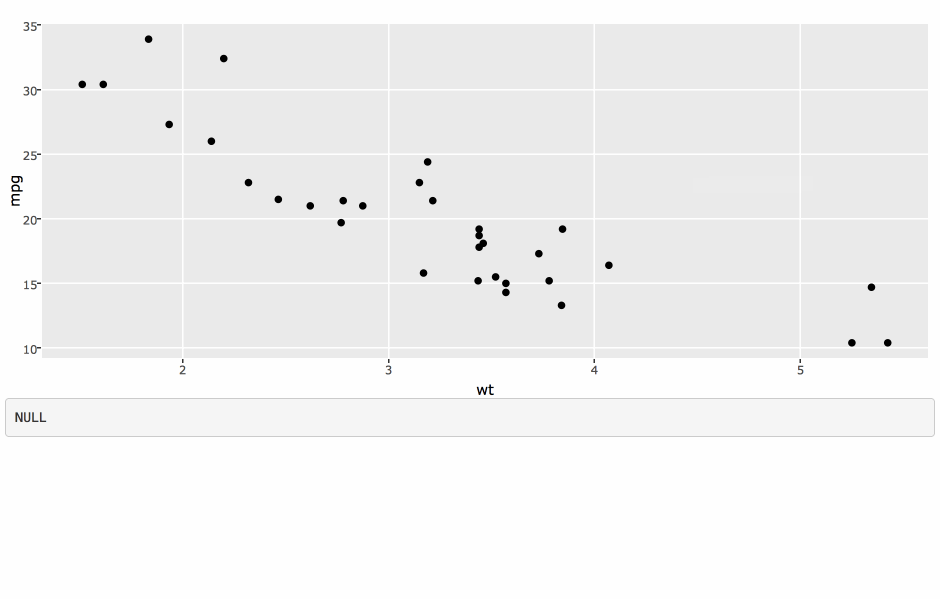
Highlighting (i.e., brushing) in multiple linked views
Highlighting via crosstalk
library(crosstalk)d <- SharedData$new(Abilene, ~year)p <- ggplot(d, aes(month, sales)) + geom_line(aes(group = year))ggplotly(p, tooltip = "year")Highlighting in small multiples
d <- subset(txhousing, city %in% c("Galveston", "Midland", "Odessa", "South Padre Island"))sd <- SharedData$new(d, ~year)p <- ggplot(sd, aes(month, median, group = year)) + geom_line() + facet_wrap(~city, ncol = 2)(gg <- ggplotly(p, tooltip = "year"))Highlight on hover
highlight(gg, "plotly_hover")Set default values
highlight(gg, defaultValues = "2006")Making comparisons with dynamic brush
highlight( gg, dynamic = TRUE, persistent = TRUE, selectize = TRUE)Customize the appearance of selections
highlight( gg, dynamic = TRUE, persistent = TRUE, selected = attrs_selected(mode = "markers+lines", marker = list(symbol = "x")))m-to-n linking
demo("highlight-pipeline", package = "plotly")Your turn
(1) Modify the last demo to have persistent and dynamic selection. Try supplying your own custom color palette.
(2) Read the code. Change add_bars() to add_markers(). How in the world does this work?
(3) Can you get this working via add_histogram()? What's the difference between using add_bars() and add_histogram()?
The 'data pipeline'
Where does the pipeline
'live'?
The general model
All the "updating logic" is self-contained in your browser via JavaScript, which is good!
Binning (i.e., transforming) the target
demo("highlight-binned-target", package = "plotly")Binning (i.e., transforming) the target
demo("highlight-binned-target", package = "plotly")You can only go so far without shiny...
...but we can combine powers
I promise...
We will get to shiny, but we can do much more without shiny1
[1]: why this is important? Ask me!
Animating selections
a <- SharedData$new(Abilene, ~month)p <- ggplot(a, aes(month, sales, frame = year)) + geom_line() + geom_point()highlight(ggplotly(p), "plotly_selected")Avoid overplotting
g <- SharedData$new(gapminder, ~continent)gg <- ggplot(g, aes(gdpPercap, lifeExp, color = continent, frame = year)) + geom_point(aes(size = pop, ids = country)) + geom_smooth(se = FALSE, method = "lm") ggplotly(gg + scale_x_log10())Filter vs selection
The highlight() function provides ways to handle/configure selection events
You can also trigger filter events through crosstalk widgets.
They are similar, but axes respond (i.e., relayout) to filter events.1
[1]: when using ggplotly(), you need to specify dynamicTicks = TRUE
Crosstalk's filtering widgets
tx <- SharedData$new(txhousing)widgets <- bscols(widths = c(12, 12, 12), filter_select("city", "Cities", tx, ~city), filter_slider("sales", "Sales", tx, ~sales), filter_checkbox("year", "Years", tx, ~year, inline = TRUE))widgetsFiltering
bscols( widths = c(4, 8), widgets, plot_ly(tx, x = ~date, y = ~median, showlegend = FALSE) %>% add_lines(color = ~city, colors = "black"))Talk to other crosstalk-enabled widgets
library(leaflet)sd <- SharedData$new(quakes)p <- plot_ly(sd, x = ~depth, y = ~mag) %>% add_markers(alpha = 0.5) %>% highlight("plotly_selected")map <- leaflet(sd) %>% addTiles() %>% addCircles()bscols(p, map)Your Turn
Add some filter widgets to the earthquakes example.
Bonus: Try saving the result to an HTML file.
Hint: You can save htmlwidgets to a self-contained HTML via htmlwidgets::saveWidget(), but this approach requires the more general htmltools::html_print()
Solution is here
Expectations vs reality

plotly has advanced support for selection events (e.g., persistent, dynamic, selectize)
Other crosstalk-enabled htmlwidgets likely won't support these additional selection event features.
However, filter events should generally be supported.
Shiny is a web application framework
Web applications are generally more powerful and flexible; but also more complicated, less responsive, and difficult to share.
Remember: examples so far can saved as self-contained HTML via htmlwidgets::saveWidget() and/or htmltools::html_print()
Accessing user events in shiny
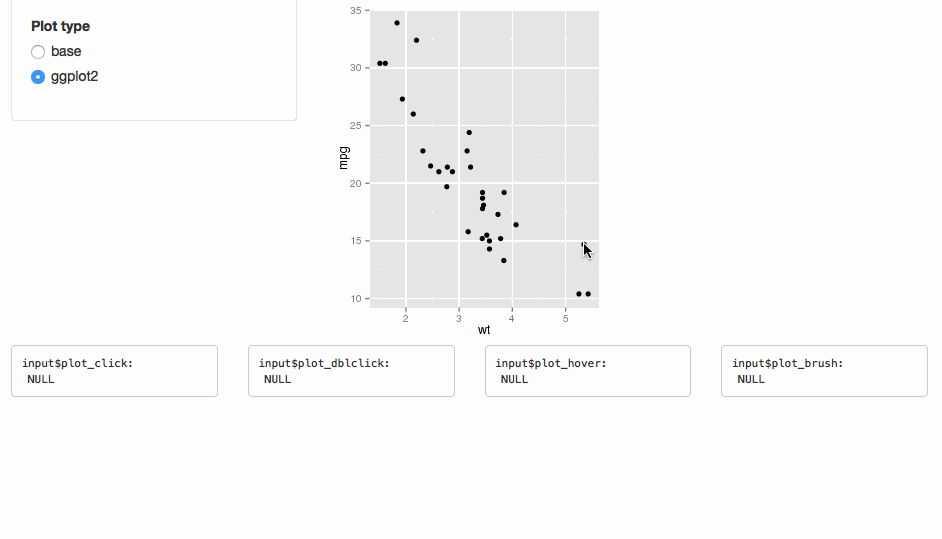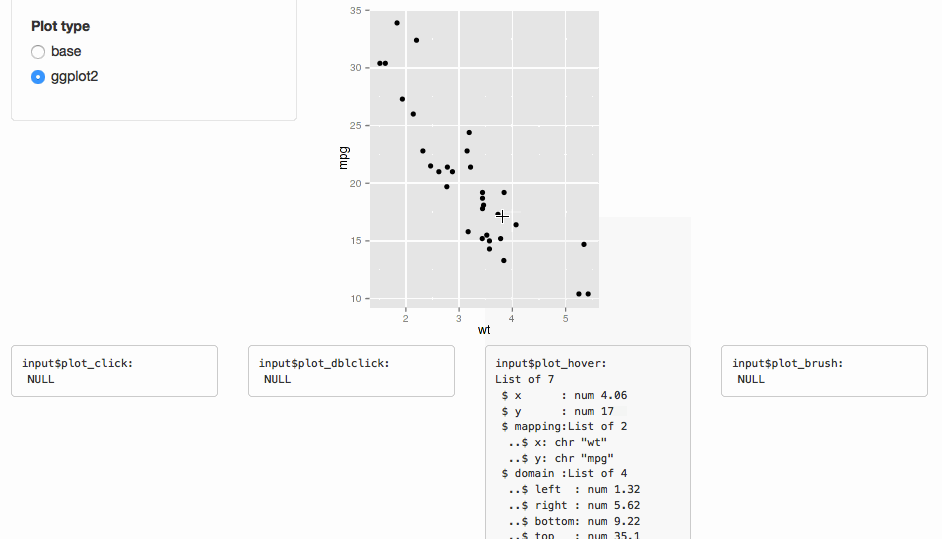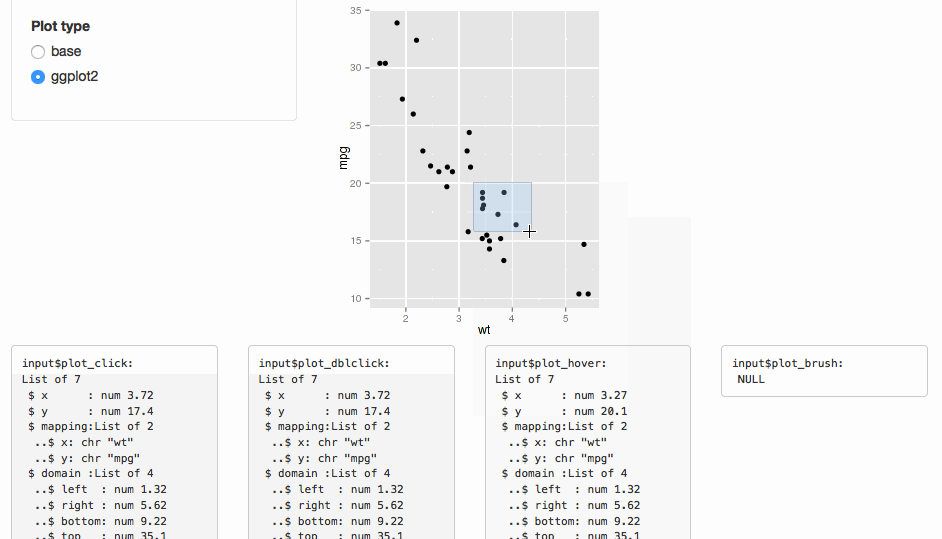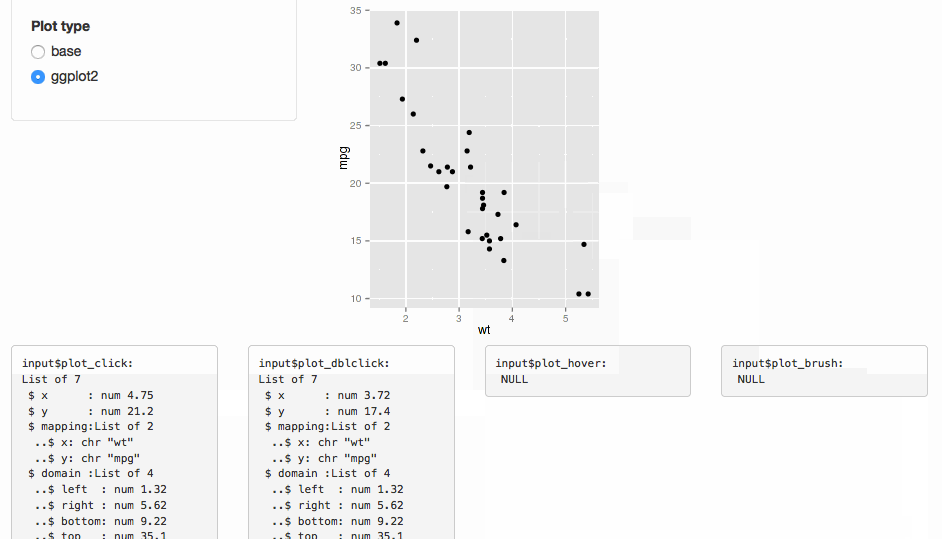
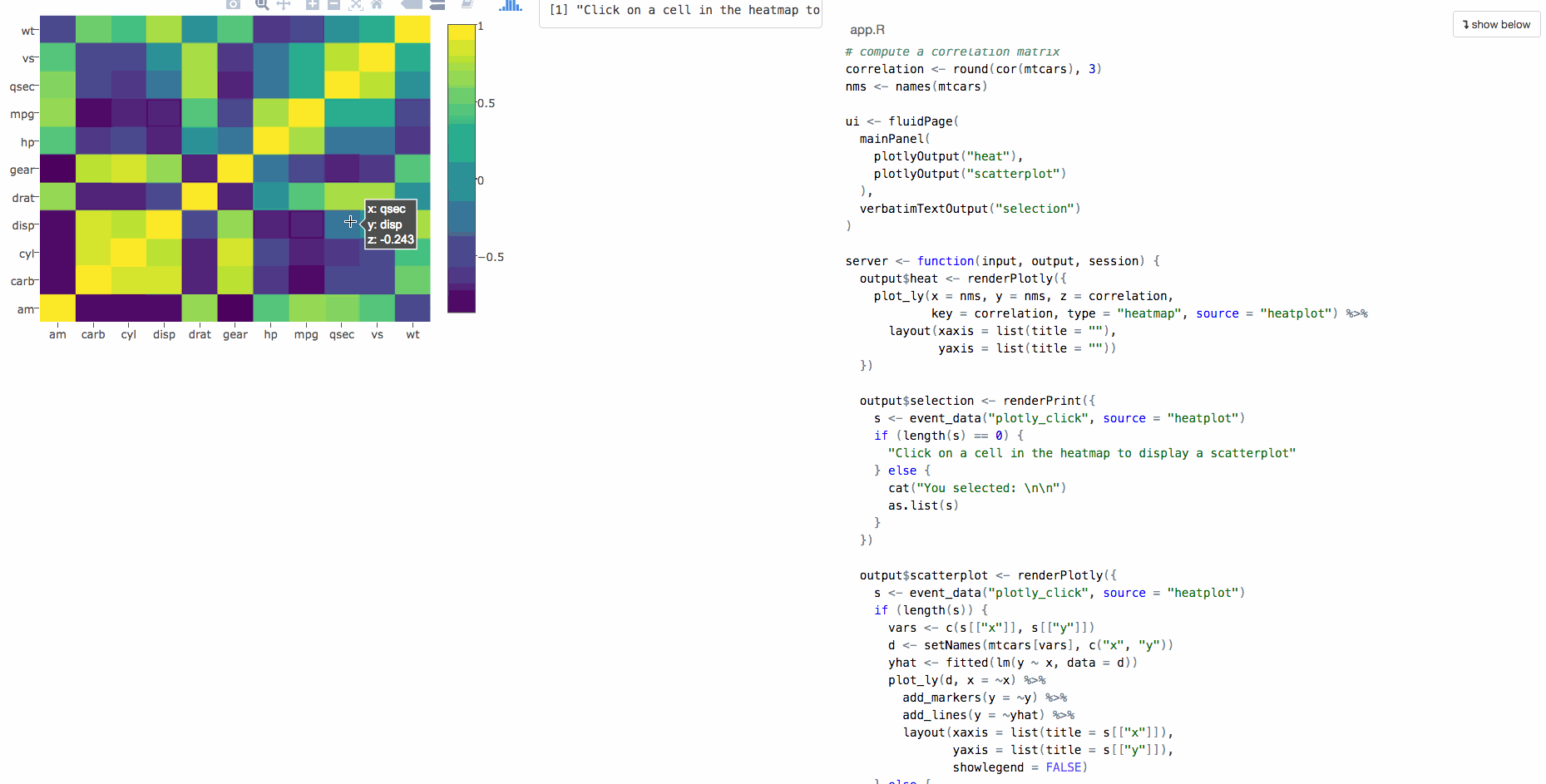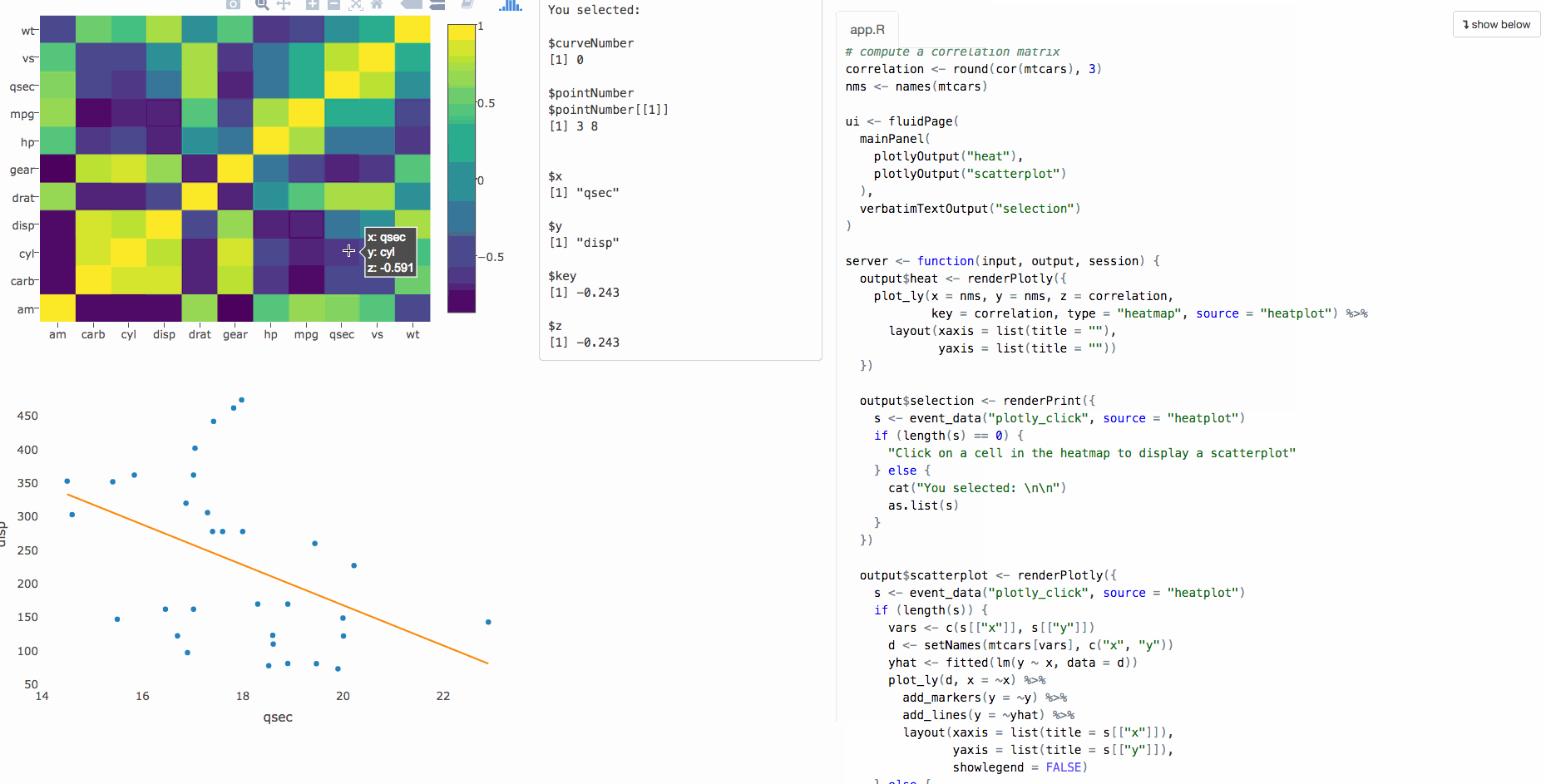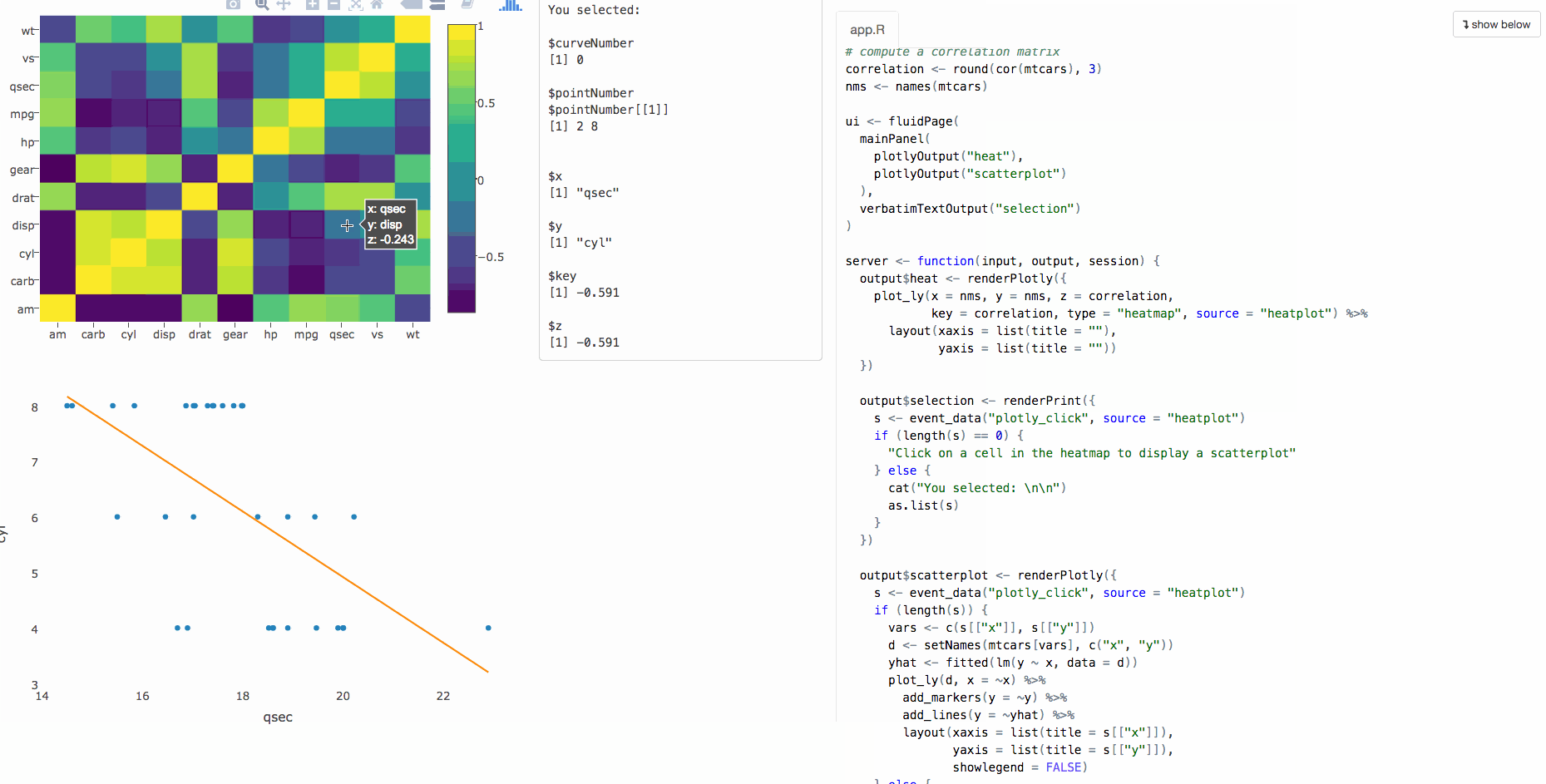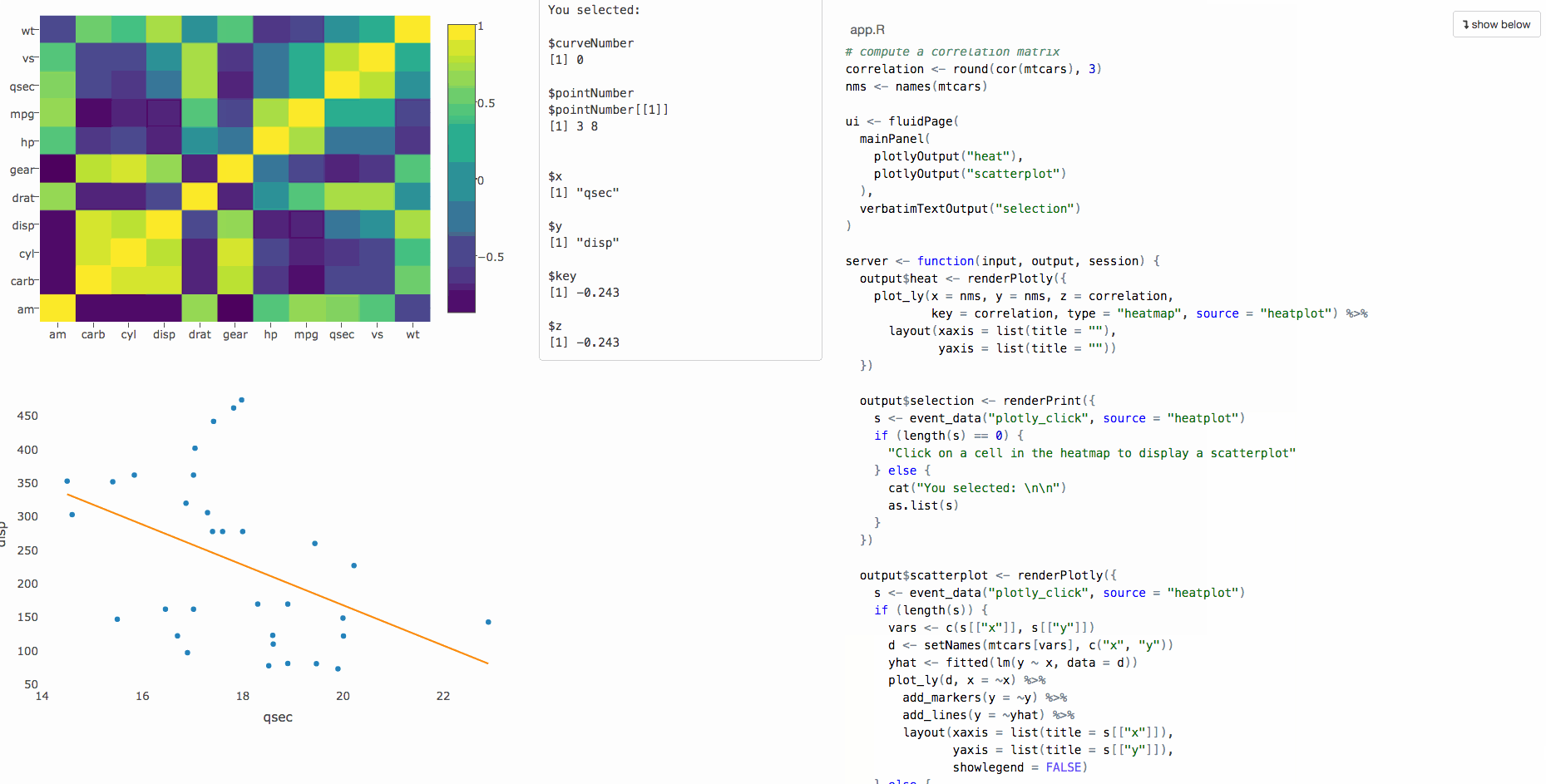
This functionality is tied to plotOutput(), which doesn't support web-based graphics.
Your Turn
Program an app to populate a bar chart reflecting the selection, sort of like this (using cars data):
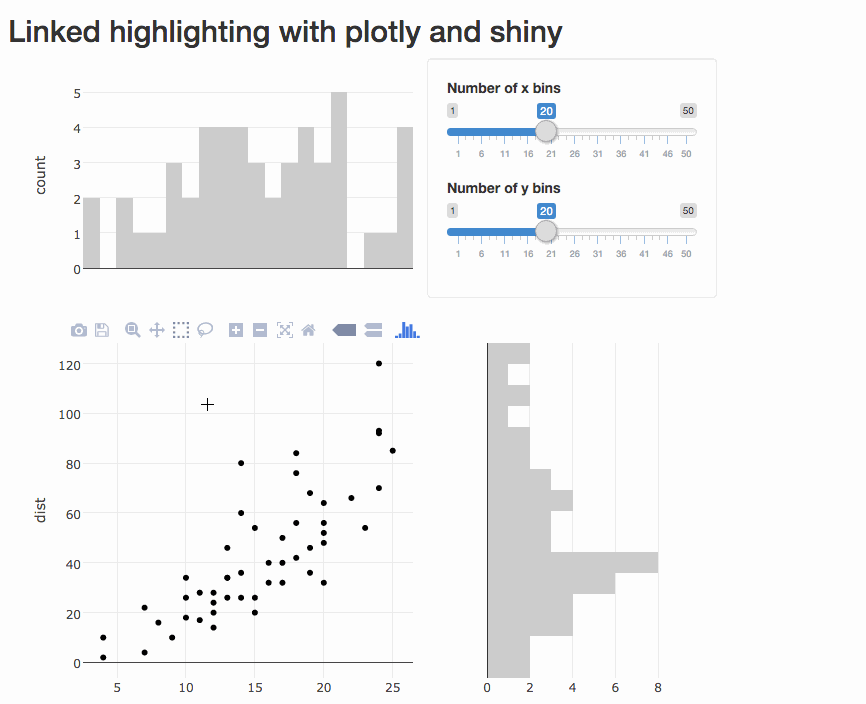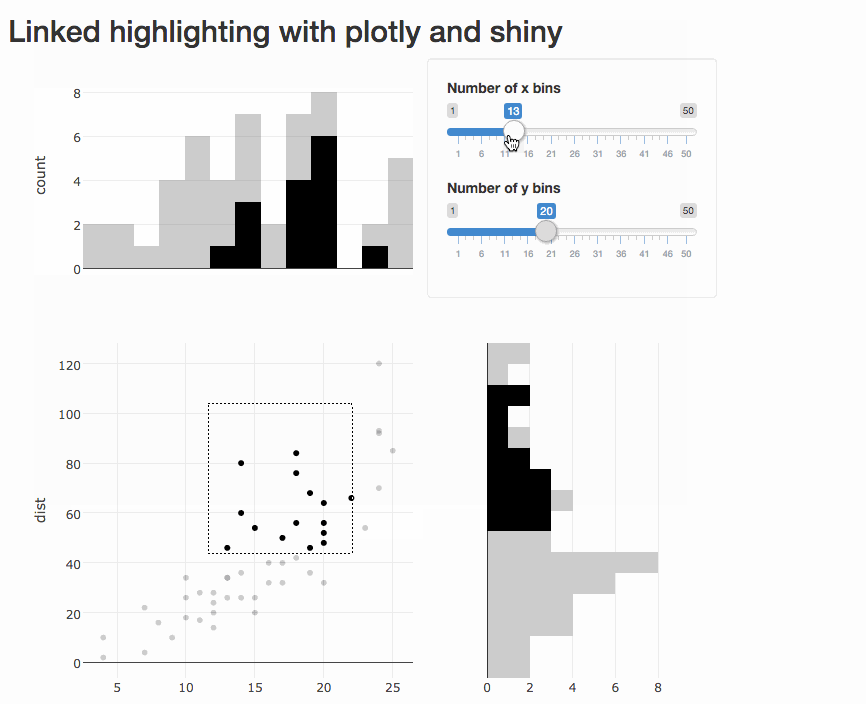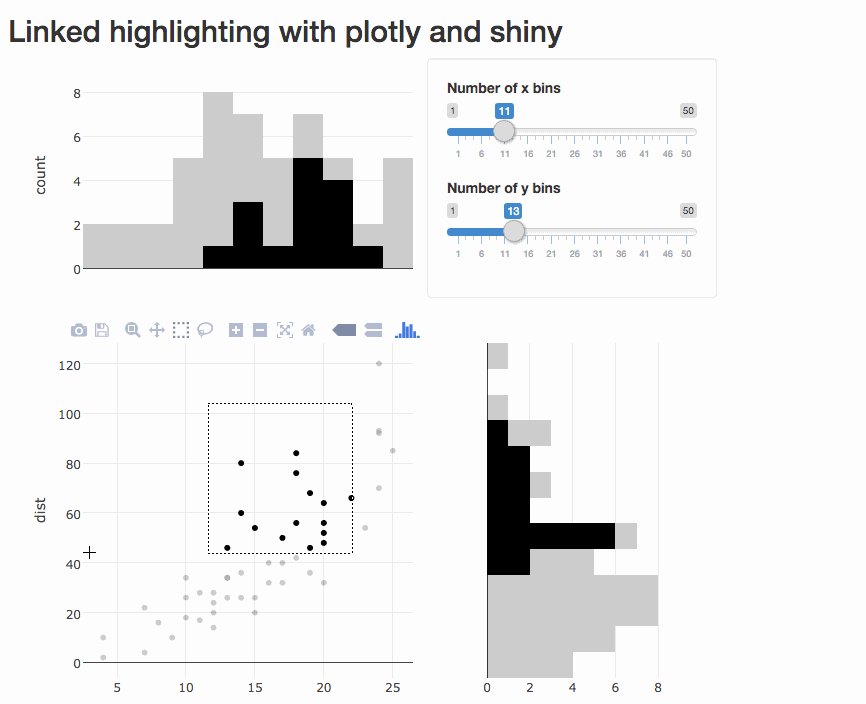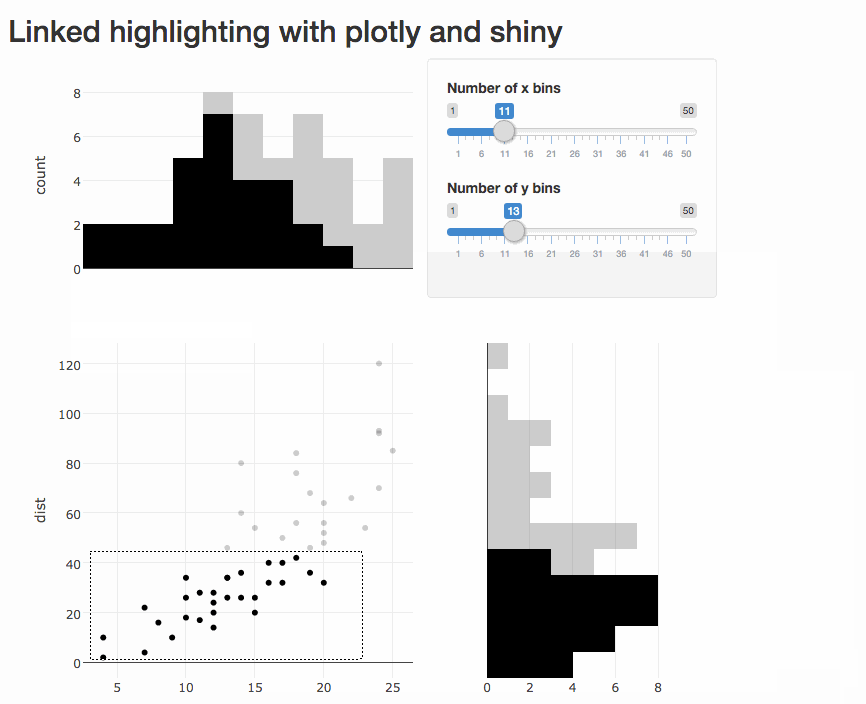
Thanks!
Resources for more learning:
https://cpsievert.github.io/plotly_book/
https://plot.ly/r/
https://cpsievert.github.io/talks/
https://github.com/cpsievert/phd-thesis
https://github.com/cpsievert/pedestrians
https://github.com/cpsievert/bcviz
https://github.com/cpsievert/shiny_apps
Reach out to me
Twitter: @cpsievert
GitHub: @cpsievert
Email: cpsievert1@gmail.com
Web: http://cpsievert.github.io/
Ask me anything!!
Want something to do? Some ideas:
- Read about the new api interface --
help(api). - Explore the demos --
demo(package = "plotly") - Read about JavaScript customization